Quantitative Data Collection: The Secret to Good Results
Quantitative data is fundamental to how business decisions are made. By using concrete numbers instead of anecdotal evidence, organizations craft more informed strategies with a higher chance of success. However, quantitative data collection isn’t easy. Businesses need to navigate a complex research process, where one wrong move can skew the results. This article explores how to gather quantitative data.
What is quantitative data?
Quantitative data is any information that is measured and communicated using numbers. It forms the backbone to statistics and data analysis. Examples of quantitative data include the number of times an event happens in a population, such as the number of births in a year.
In market research, data collection techniques for quantitative research include online surveys or structured interviews via phone or video. In its simplest form, it could gather responses from people on whether they agree or disagree with a statement. The raw data is often analyzed using statistical methods and advanced analytics to gain insight into patterns and trends. If the sample used is statistically significant in size and representative of the target market, then those insights can be applied to a broader population.
This contrasts with qualitative data, which is descriptive information often gathered through in-depth phone or video interviews or focus groups, with a smaller number of individuals. Quantitative data is considered more objective because it gathers input from a larger and more diverse number of individuals. Therefore, it is less open to personal interpretation. However, it is still possible for the data to be biased depending on how it is collected.
How is it used?
In highly competitive markets, quantitative data gives businesses an edge over their competitors. It is used to analyze market and economic trends, and to inform business strategy. Without accurate data, strategies become speculative at best.
There are several advantages to using quantitative data to inform decision making:
- Objective insights: Numbers provide an unbiased view of market dynamics.
- Trend analysis: Helps spot emerging opportunities and potential threats.
- Predictive power: Past data can forecast future market or customer behavior.
- Measurable outcomes: Facilitates comparison and evaluation.
Data is very important for various job functions in an organization. This includes marketing, product development, sales and business development, and customer support, among others. Making decisions based on customer feedback boosts the chances of success. These decisions can lead to millions of dollars in spending on capital projects or marketing. Therefore, it is crucial to make the right choice.
Common uses for quantitative data in marketing include:
- Brand tracking: Measuring brand awareness and perception in the market
- Customer experience: Tracking the impact of key initiatives on customer satisfaction using metrics like Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Market segmentation: Grouping customers based on behaviors, attitudes, values, or needs
- Product development: Assessing customers’ needs, reactions to new innovations, and whether they will pay more for certain product features
- Market intelligence: Identifying key market opportunities based on how customer needs are being met by existing solutions
How to collect quantitative data
It is critical to use the right quantitative data collection methods and tools. A poorly worded survey or fraudulent data could bias the responses.
Many businesses hire a B2B market research agency that specializes in quantitative research to make sure that the data collected is both reliable and accurate. However, this is not a guarantee, as the rates of data fraud in market research show.
Data collection methods in quantitative research
There are two key data gathering methods in quantitative research: online surveys and structured interviews via phone using CATI or video call. Let’s explore the pros and cons of each method.
Online surveys
Online surveys are administered online using specialized survey software. They are often favored as one of the ways of collecting quantitative data because they are easy and cheap to run. However, there is a greater risk that the data will be of poor quality or fraudulent.
Pros of online surveys
- Easy to administer through survey software.
- The survey taker completes the survey at their own pace, clicking through to the next screen once they have answered a question.
- They are cheaper: the survey is self-administered and therefore doesn’t require paying an interviewer.
Cons of online surveys
- Since there is no one helping the respondent with the survey, it is easier for them to misunderstand a question or hurry through their answers. This results in more inaccurate data.
- It is hard to confirm who is taking the survey. Because of this, fraud in online surveys is very common.
- The Insights Association estimates that 43% of online survey data is rejected by market research agencies for this reason.
- Technical problems with online survey software can lead to bad experiences for people taking surveys. This can harm both the quality and amount of data collected.
Structured interviews conducted via phone or video call
Structured interviews are where an interviewer asks a participant a series of predetermined questions. They are often conducted via phone using CATI (computer assisted telephone interviews), or video conferencing software. It is an effective way to gather quantitative data from a large group of participants, while also maintaining high standards of data quality.
Pros of structured interviews
- Standardization minimizes interviewer bias and enhances the comparability of responses.
- It is easier to validate the identity of respondents via phone or video calls, reducing the risk of data fraud.
- The interviewer makes sure the respondent doesn’t rush through their answers. This reduces the amount of poor quality data.
- Interviewers can follow up or provide additional clarity if a respondent is confused by a question.
Cons of structured interviews
- They cost more to administer since it requires paying an interviewer for their time.
- It can take longer to gather data.
The data collection procedure in quantitative research
A structured data collection procedure in quantitative research is essential. This ensures consistency and reliability in the results.
It is important to consider the following:
- Data collection method: Which of the quantitative data gathering techniques is most appropriate?
- Data quality: How reliable are your data sources? Do you have safeguards in place to prevent fraud?
- Sample size: What sample size is needed for your research to be statistically significant?
- Incentives: What level of incentive is needed to motivate your audience to participate in a survey or interview?
- Sample plan and quotas: How can you make the data representative of your target market and do you need insight into the differences between customer segments?
Step-by-step guide to the data collection process
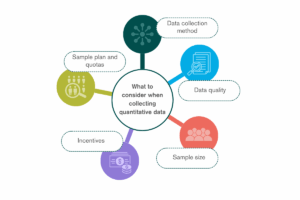
Here are six steps to data collection:
- Define your research objectives: Start by defining your research objectives. What are you looking to achieve from your research study? What research methods will you use? Knowing your goals will guide the choice of methods, tools, and audience sample.
- Decide on your data collection method: Consider factors such as your target audience and available resources. Some audiences are hard to reach online and are better contacted by phone. This is especially true for B2B experts, where it’s important to confirm their identity.
- Determine your target audience and sample size: You will need your sample to be representative of your audience. Best practice dictates that it should be statistically significant. You can use a sample size calculator to determine the ideal sample size.
- Design a questionnaire: A user-friendly design and carefully worded questions mitigates the risk of bias and improves response rates.
- Field the questionnaire: It’s crucial to pilot questionnaires before full deployment. Pre-testing helps identify potential issues that could skew results. After refinement, proceed with the data collection. Ensure strict adherence to ethical standards, obtaining informed consent from participants.
- Validate and clean the data: Check the data for indications of fraud and remove incomplete or poor-quality responses.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
Quantitative data collection can be fraught with pitfalls that compromise research integrity.
One common mistake is unclear survey questions. For instance, asking respondents to rank multiple attributes in one go (e.g., “Would you describe the brand as cheap and efficient?”) makes it hard to distinguish what actually matters.
Overly complicated and long-winded questions can also lead to poor data if participants misunderstand or simply rush through their answers.
Another problem is making sure the sample is not only big enough to be statistically significant, but also representative of different audience segments where necessary (e.g., age, gender, location, job).
Here are some common pitfalls to avoid in data collection:
- Unrepresentative sample
- Poorly worded and illogical questions
- Biased and leading data collection techniques
- Lack of sufficient data validation
- Technical issues with the data collection software
- Problems with the survey design, such as unreadable fonts
Steering clear of these pitfalls makes sure that you collect reliable and sound data.
Why questionnaire design is important
Questionnaires are a series of standardized questions that are used to gather large volumes of quantitative data. They form the basis for data gathering methods for quantitative research, such as online surveys and structured interviews via phone or video.
A poorly worded questionnaire can fall prey to low engagement and biased responses. Designing effective questionnaires, therefore, requires thoughtful consideration of multiple factors:
- Clarity: Concise and simple language leads to better understanding of the questions among participants
- Precision: It’s important to be specific. Ambiguous wording or overlapping options distort the data.
- Complexity: Matrix questions that ask participants to rank or score several items at once can raise the chance of low engagement or incorrect responses.
- Length: A shorter questionnaire will have a higher completion rate. Too many questions cause participants to lose focus and drop out.
- Question bias: Unbiased questions and balanced options lead to representative data.
- Selection Bias: Randomizing the order of multiple-choice answers allows us to see whether participants are genuinely considering the question or just choosing the first option available.
The complexity of questionnaire design for quantitative research studies often leads companies to hire a specialized market research agency. The agency is experienced in designing the questionnaire, ensuring questions and attributes are mutually exclusive but collectively exhaustive (MECE), gathering the responses and analyzing the data, and can therefore avoid accidental biases in the research.
Quantitative data collection tools
If you are looking for a DIY way to collect quantitative data, there are several quantitative data collection tools available in the market.
Selecting the best tool is crucial to research success. However, there are limitations to these tools, and many research studies fail for the reasons outlined above.
- Qualtrics: A cloud-based survey software platform that enables you to create, distribute, and analyze surveys. It has many features that allow for customization, but this makes it more complicated to use than simpler options.
- Q Research Software: A survey and data analysis platform designed and used by B2B market research companies for comprehensive market research. Its advanced features make it particularly suitable for effectively processing and analyzing survey data. However, the platform is not intuitive, and there is a steep learning curve.
- SurveyMonkey: A popular survey design and distribution tool. Its simple user interface and lower cost make it a popular option for those who only send surveys sometimes or don’t need much customization.
When to hire a research agency
If you need to carry out a big research study or reach a specific group of people, it makes sense to hire a research agency. Full-service market research companies like Werk Insight provide end-to-end research.
The end-to-end research process includes designing custom questionnaires and fielding them with your target audience. The data is analyzed to find useful insights, which are presented in a report with clear recommendations.
This holistic research approach is often more successful in meeting an organization’s goals.
Key advantages of end-to-end research
Here are some of the advantages of working with an agency when designing a quantitative research study:
Surveys or interviews done by a third party help you ask about sensitive topics while keeping your identity hidden.
- Reduces the risk of fabricated or fraudulent data
- Better alignment between the questions and research goals
- Clearer and more precise questions thanks to deep industry knowledge, such as key terms, market trends and regulations
- Using qualitative methods like focus groups and in-depth interviews can help shape the design of questionnaires. These methods provide rich insights that guide the questions asked, ensuring they meet the needs of the research.
- More thoughtful study design lowers the risk of bias and forced errors
- Analysis of the data using advanced analytics unearths valuable insights
How to choose a research agency
When choosing a research agency to work with, evaluate their depth of expertise in your specific industry. For instance, a B2B company should look for a B2B market research company with experience in their vertical.
- Industry directories like Greenbook are a good starting point when searching for an agency with relevant experience.
- Case studies can tell you if a research agency has conducted similar research in the past
- Testimonials from former clients validate the agency’s success in delivering impactful research
Data validation: the missing link in most research
Data validation is an integral part of data collection because it safeguards against fraudulent and flawed data. A strategy based on flawed data is more likely to fail, which can actively harm a business. Put simply, unvalidated data could lead to costly errors.
Fraud in online surveys
Fraudulent responses in online surveys is a growing concern. The Insights Association recently found that 43% of responses from online surveys are rejected by research agencies. Unvalidated respondents might provide inaccurate data, whether intentionally or by mistake. This can skew the research findings.
Fraudsters are highly motivated to take online surveys because the rewards can be anywhere from a few dollars to several hundred dollars.
In some cases, data fraud is organized; bots target online surveys to harvest incentives on a large scale.
Fraud can also happen when someone takes a survey but isn’t qualified. They may know enough to get past the screening questions that check if they should be answering the survey.
Data validation methods
Online surveys often include screening questions that are designed to filter out unqualified respondents. On a basic level, this can include factors such as job title or qualifications. A well-designed survey will include questions that test the respondent’s familiarity with the subject matter.
However, AI and machine learning are making it simpler for fraudsters to imitate experts and bypass these screening questions.
Advanced technological solutions promise to detect fraud in online survey responses once they have been collected. This can include:
- Flagging multiple responses from the same IP address or geolocation
- Collecting survey responses via mobile devices
- Cross checking responses for consistency and logic
- Using AI to identify patterns of fraud
However, this is not failproof. Fraud evolves and sophisticated fraudsters can find ways around these checks.
Werk Insight thinks the best way to reduce fraud is by using structured interviews done over the phone or video.
This way the expert’s identity can be validated face-to-face. Checking a respondent’s identity with a business email address or a government ID also helps to ensure that they are legitimate.
Proactive data validation boosts research reliability. Implementing strong fraud prevention measures makes sure that business strategies are informed by sound, trustworthy data.
Conclusion: business strategies are built on solid data
Robust quantitative data collection is the foundation to sound business strategy. It is the mechanism for gathering data that can be relied on to make critical decisions. Flawed data can lead to costly mistakes, especially if it is not validated.
Growing fraud in the industry is making it even more important to invest in solid data collection practices. Businesses that recognize the value of data integrity will benefit from more informed strategies, underpinning sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Construction Materials Company Drives Growth Through Improved Customer Experience
A construction materials company wanted to drive growth through improving its customer experience among its customer base of industrial manufacturers and installers. The...